Why can't I take insulin as a pill?
Insulin is a protein. If you took insulin as a pill, your body would break it down and digest it before it got into your blood to lower your blood sugar.
How does insulin work?
Insulin lowers blood sugar by moving sugar from the blood into the cells of your body. Once inside the cells, sugar provides energy. Insulin lowers your blood sugar whether you eat or not. You should eat on time if you take insulin.
How often should I take insulin?
Most people with diabetes need at least two insulin shots a day for good blood sugar control. Some people take three or four shots a day to have a more flexible diabetes plan.
When should I take insulin?
You should take insulin 30 minutes before a meal if you take regular insulin alone or with a longer-acting insulin. If you take insulin lispro (Humalog), an insulin that works very quickly, you should take your shot just before you eat.
Are there several types of insulin?
Yes. There are five main types of insulin. They each work at different speeds. Many people take two types of insulin.
The five types of insulin are
Quick acting, insulin lispro (Humalog)
Starts working in 5 to 15 minutes.
Lowers blood sugar most in 45 to 90 minutes.
Finishes working in 3 to 4 hours.Short acting, Regular (R) insulin
Starts working in 30 minutes.
Lowers blood sugar most in 2 to 5 hours.
Finishes working in 5 to 8 hours.Intermediate acting, NPH (N) or Lente (L) insulin
Starts working in 1 to 3 hours.
Lowers blood sugar most in 6 to 12 hours.
Finishes working in 16 to 24 hours.Long acting, Ultralente (U) insulin
Starts working in 4 to 6 hours.
Lowers blood sugar most in 8 to 20 hours.
Finishes working in 24 to 28 hours.NPH and Regular insulin mixture
Two types of insulins mixed together in one bottle.
Starts working in 30 minutes.
Lowers blood sugar most in 7 to 12 hours.
Finishes working in 16 to 24 hours.
Does insulin work the same all the time?
After a short time, you will get to know when your insulin starts to work, when it works its hardest to lower blood sugar, and when it finishes working.
You will learn to match your mealtimes and exercise times to the time when each insulin you take works in your body.
How quickly or slowly insulin works in your body depends on:
- Your own response.
- The place on your body where you inject insulin.
- The type and amount of exercise you do and the length of time between your shot and exercise.
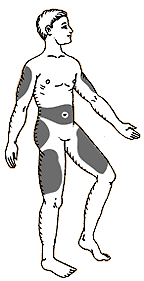
Where on my body should I inject insulin?
You can inject insulin into several places on your body. Insulin injected near the stomach works fastest. Insulin injected into the thigh works slowest.
Insulin injected into the arm works at medium speed. Ask your doctor or diabetes teacher to show you the right way to take insulin and in which parts of the body to inject it.
|
How should I store insulin?
|
- If you use a whole bottle of insulin within 30 days, keep that bottle of insulin at room temperature. On the label, write the date that is 30 days away. That is when you should throw out the bottle with any insulin left in it.
- If you do not use a whole bottle of insulin within 30 days, then store it in the refrigerator all the time.
- If insulin gets too hot or cold, it breaks down and does not work. So, do not keep insulin in very cold places such as the freezer, or in hot places, such as by a window or in the car's glove compartment during warm weather.
- Keep at least one extra bottle of each type of insulin you use in your house. Store extra insulin in the refrigerator.
What are possible side effects of insulin?
- A low blood sugar reaction (hypoglycemia).
- Weight gain.
NIDDK