Carbohydrates are one of the main nutrients found in the food and drinks we consume. Protein and fat are the other main nutrients. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and fiber.
Carbohydrate counting can help you control your blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar levels, because carbohydrates affect your blood glucose more than the other nutrients.
Healthy carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are an important part of a healthy meal plan because they can provide both energy and nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, and fiber. Fiber can help you prevent constipation, lower your cholesterol levels, and control your weight.
Unhealthy carbohydrates are often food and drinks with added sugars. Added sugars are various forms of sugar added to foods or drinks during processing or preparation. Naturally occurring sugars such as those in milk and fruits are not added sugars but are carbohydrates. Although unhealthy carbohydrates can also provide energy, they have little to no nutrients.
The amount of carbohydrate in foods is measured in grams.
To count grams of carbohydrate in foods you eat, you’ll need to:
- know which foods contain carbohydrates
- learn to estimate the number of grams of carbohydrate in the foods you eat
- add up the number of grams of carbohydrate from each food you eat to get your total for the day
Your doctor can refer you to a dietitian or diabetes educator who can help you develop a healthy eating plan based on carbohydrate counting.
The Amount of Carbohydrates a Diabetic Needs Each Day
The daily amount of carbohydrate, protein, and fat for people with diabetes has not been defined because what is best for one person may not be best for another. Everyone needs to get enough carbohydrate to meet the body’s needs for energy, vitamins and minerals, and fiber.
Experts suggest that carbohydrate intake for most people should be between 45 and 65 percent of total calories. People on low-calorie diets and people who are physically inactive may want to aim for the lower end of that range.
One gram of carbohydrate provides about 4 calories, so you’ll have to divide the number of calories you want to get from carbohydrates by 4 to get the number of grams.
For example, if you want to eat 1,800 total calories per day and get 45 percent of your calories from carbohydrates, you would aim for about 200 grams of carbohydrate daily.
You would calculate that amount as follows:
.45 x 1,800 calories = 810 calories
810 ÷ 4 = 202.5 grams of carbohydrate
You’ll need to spread out your carbohydrate intake throughout the day. A dietitian or diabetes educator can help you learn what foods to eat, how much to eat, and when to eat based on your weight, activity level, medicines, and blood glucose targets.
How to find out how much carbohydrate is in the foods you eat
People with diabetes need to learn how to estimate the amount of carbohydrate in the foods they typically eat.
For example, the following amounts of carbohydrate-rich foods each contain about 15 grams of carbohydrate:
- 1/2 cup of pinto beans
- one slice of bread
- 3/4 cup of dry cereal or 1/2 cup cooked cereal
- one 6-inch tortilla
- 1/3 cup of pasta
- 1/3 cup of rice
- 1/2 cup of canned or fresh fruit or fruit juice or one small piece of fresh fruit, such as a small apple or orange
- 1/2 cup of starchy vegetables such as mashed potatoes, cooked corn, peas, or lima beans
- 1 tablespoon of jelly
Some foods are so low in carbohydrates that you may not have to count them unless you eat large amounts. These are commonly referred to as “free foods.”
For example, most non-starchy vegetables are low in carbohydrates. A 1/2-cup serving of cooked nonstarchy vegetables or a cup of raw vegetables has only about 5 grams of carbohydrate. Example free foods include cucumber slices, celery and tomato salsa.
As you become familiar with which foods contain carbohydrates and how many grams of carbohydrate are in food you eat, carbohydrate counting will be easier.
Nutrition Labels and Carbohydrate Counting
You can find out how many grams of carbohydrate are in the foods you eat by checking the nutrition labels on food packages.
Here is an example of a nutrition label:
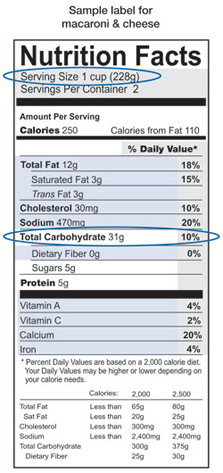
In the sample nutrition label above for macaroni and cheese, it shows a serving size of 1-cup and a total carbohydrate amount of 31 grams.
Nutrition labels tell us:
- the food’s serving size – such as one slice or 1/2 cup
- the total grams of carbohydrate per serving
- other nutrition information, including calories and the amount of protein and fat per serving
If you have two servings instead of one, such as one cup of pinto beans instead of 1/2 cup, you multiply the number of grams of carbohydrate in one serving. In this example, 15 multiplied by two get the total number of grams of carbohydrate (30).
15 x 2 = 30
Checking your blood glucose levels can help you tell whether carbohydrate counting is working for you. You can check your blood glucose levels using a glucose meter. You should also have an A1C blood test at least twice a year. The A1C test reflects the average amount of glucose in your blood during the past 3 months.
If your blood glucose levels are too high, you may need to make changes in your eating plan or other lifestyle changes. For example, you may need to make wiser food choices, be more physically active, or make changes to your diabetes medicines. Talk with your doctor about what changes you need to make to control your blood glucose levels.








